Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molecular Compounds
Molecular compounds are formed when two or more nonmetals bond together by sharing electrons. They typically have distinct properties, such as lower melting and boiling points compared to ionic compounds. The naming of molecular compounds often involves using prefixes to indicate the number of atoms of each element present in the compound.
Recommended video:
Naming Molecular Compounds
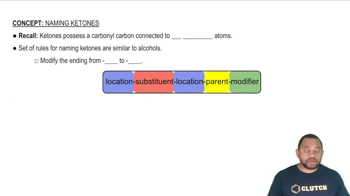
Naming Conventions
The naming of molecular compounds follows specific conventions, primarily using prefixes to denote the number of atoms. For example, 'mono-' for one, 'di-' for two, 'tri-' for three, and so on. The first element in the compound is named first, followed by the second element, which is modified to end in '-ide'.
Recommended video:
Chemical Symbols and Formulas
Chemical symbols represent elements, while chemical formulas indicate the composition of a compound. For instance, 'CO' represents carbon monoxide, where 'C' is carbon and 'O' is oxygen. Understanding these symbols and how they combine is essential for correctly identifying and naming molecular compounds.
Recommended video: