Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons are organic compounds consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. They can be classified into aliphatic (straight or branched chains) and aromatic (ring structures with delocalized electrons). Ethylbenzene, for example, is an aromatic hydrocarbon that contains a benzene ring and an ethyl group, illustrating the combination of these two types.
Recommended video:
Functional Groups
Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. In ethylbenzene, the presence of the ethyl group (-C2H5) attached to the benzene ring influences its reactivity and properties, making it important to recognize when drawing its structure.
Recommended video:
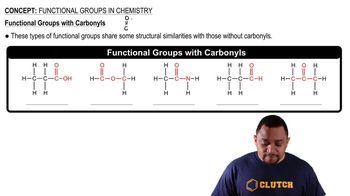
Carbonyl Functional Groups
Structural Representation
Structural representation refers to the way in which the arrangement of atoms in a molecule is depicted. For ethylbenzene, this involves illustrating the benzene ring with alternating double bonds and the ethyl group attached to one of the carbon atoms in the ring. Understanding how to accurately represent these structures is crucial for visualizing and predicting the behavior of organic compounds.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance