Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Alkanes
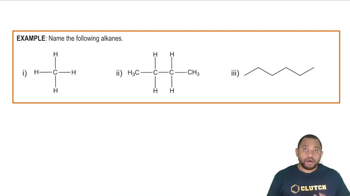
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons consisting only of carbon (C) and hydrogen (H) atoms, connected by single bonds. They follow the general formula CnH2n+2, where 'n' is the number of carbon atoms. Alkanes are characterized by their relatively low reactivity and are commonly found in natural gas and petroleum.
Recommended video:
IUPAC Nomenclature
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) nomenclature provides a systematic way to name chemical compounds. For alkanes, the name reflects the longest continuous carbon chain and any substituents. In the case of 3-ethyl-3-methylpentane, 'pentane' indicates a five-carbon chain, while '3-ethyl' and '3-methyl' denote the positions and types of branches on the chain.
Recommended video:
Structural Representation
Structural representation of alkanes involves illustrating the arrangement of atoms and bonds in a molecule. This can be done using line-angle formulas, where lines represent bonds between carbon atoms, and vertices represent carbon atoms. Understanding how to draw these structures is essential for visualizing molecular geometry and predicting chemical behavior.
Recommended video: