Consider the exothermic reaction: C2H4(g) + Cl2(g) ⇌ C2H4Cl2(g) If you were trying to maximize the amount of C2H4Cl2 produced, which tactic might you try? Assume that the reaction mixture reaches equilibrium. a. increasing the reaction volume b. removing C2H4Cl2 from the reaction mixture as it forms c. lowering the reaction temperature d. adding Cl2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Le Chatelier's Principle

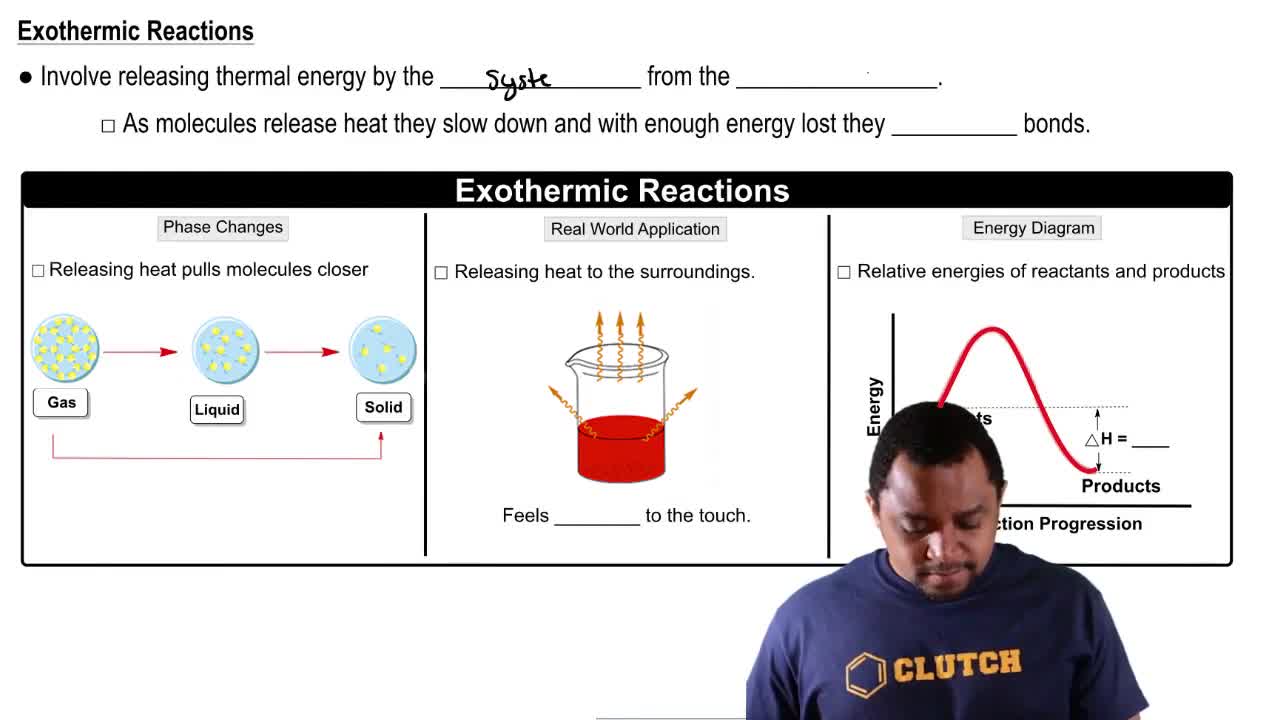
Exothermic Reactions
Equilibrium Constant (K)

At 650 K, the reaction MgCO3(s) ⇌ MgO(s) + CO2(g) has Kp = 0.026. A 10.0-L container at 650 K has 1.0 g of MgO(s) and CO2 at P = 0.0260 atm. The container is then compressed to a volume of 0.100 L. Find the mass of MgCO3 that is formed.
Consider the endothermic reaction: C2H4(g) + I2(g) ⇌ C2H4I2(g) If you were trying to maximize the amount of C2H4I2 produced, which tactic might you try? Assume that the reaction mixture reaches equilibrium. a. decreasing the reaction volume b. removing I2 from the reaction mixture c. raising the reaction temperature d. adding C2H4 to the reaction mixture
Consider the reaction: H2(g) + I2(g) ⇌ 2 HI(g) A reaction mixture at equilibrium at 175 K contains PH2 = 0.958 atm, PI2 = 0.877 atm, and PHI = 0.020 atm. A second reaction mixture, also at 175 K, contains PH2 = PI2 = 0.621 atm and PHI = 0.101 atm. Is the second reaction at equilibrium? If not, what will be the partial pressure of HI when the reaction reaches equilibrium at 175 K?
