Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
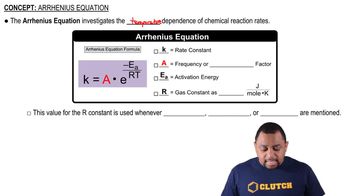
Arrhenius Equation
The Arrhenius equation describes how the rate constant of a chemical reaction depends on temperature and activation energy. It is expressed as k = A * e^(-Ea/RT), where k is the rate constant, A is the frequency factor, Ea is the activation energy, R is the universal gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvin. This relationship highlights the exponential increase in reaction rates with temperature, making it essential for analyzing reaction kinetics.
Recommended video:
Activation Energy (Ea)
Activation energy is the minimum energy required for a chemical reaction to occur. It represents the energy barrier that reactants must overcome to transform into products. In an Arrhenius plot, which is a graph of ln(k) versus 1/T, the slope of the line is related to -Ea/R, allowing for the determination of the activation energy from experimental data.
Recommended video:
Frequency Factor (A)
The frequency factor, also known as the pre-exponential factor, is a constant in the Arrhenius equation that reflects the frequency of collisions and the orientation of reactants during a reaction. It is indicative of how often reactants collide with the correct orientation to react. The frequency factor can be determined alongside the activation energy when analyzing the slope and intercept of the Arrhenius plot.
Recommended video:
Frequency-Wavelength Relationship