The data shown here were collected for the first-order reaction: N2O(g) → N2(g) + O(g) Use an Arrhenius plot to determine the activation barrier and frequency factor for the reaction.
Temperature (K) Rate Constant (1 , s)
800 3.24⨉10- 5
900 0.00214
1000 0.0614
1100 0.955

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
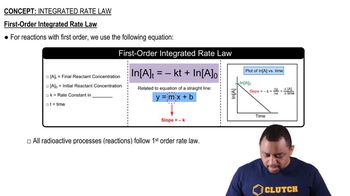
First-Order Reactions
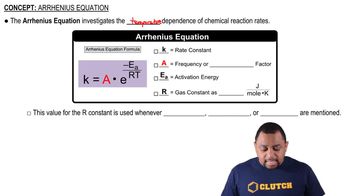
Arrhenius Equation
Activation Energy

The rate constant (k) for a reaction was measured as a function of temperature. A plot of ln k versus 1/T (in K) is linear and has a slope of -7445 K. Calculate the activation energy for the reaction.
The tabulated data show the rate constant of a reaction measured at several different temperatures. Use an Arrhenius plot to determine the activation barrier and frequency factor for the reaction.
Temperature (K) Rate Constant (1 , s)
300 0.0134
310 0.0407
320 0.114
330 0.303
340 0.757
The tabulated data show the rate constant of a reaction measured at several different temperatures. Use an Arrhenius plot to determine the activation barrier and frequency factor for the reaction.
Temperature (K) Rate Constant (1 , s)
310 0.00434
320 0.0140
330 0.0421
340 0.118
350 0.316
