Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Rate Constant
The rate constant (k) is a proportionality factor in the rate law of a chemical reaction, indicating the speed of the reaction at a given temperature. It is specific to each reaction and varies with temperature, reflecting how the reaction's rate changes under different conditions.
Recommended video:
Arrhenius Equation
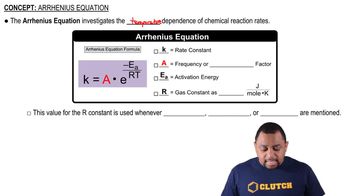
The Arrhenius equation describes the temperature dependence of the rate constant, expressed as k = A * e^(-Ea/RT), where A is the pre-exponential factor, Ea is the activation energy, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvin. This equation allows for the calculation of rate constants at different temperatures by relating them through their activation energy.
Recommended video:
Temperature Conversion
In chemical kinetics, temperatures must often be converted to Kelvin for calculations. The conversion from Celsius to Kelvin is done by adding 273.15 to the Celsius temperature. Accurate temperature conversion is crucial for applying the Arrhenius equation and determining the rate constant at different temperatures.
Recommended video:
Temperature Conversion Example