A saturated solution forms when 0.0537 L of argon, at a pressure of 1.0 atm and temperature of 25 °C, is dissolved in 1.0 L of water. Calculate the Henry's law constant for argon.
Ch.13 - Solutions
Chapter 13, Problem 106
Water softeners often replace calcium ions in hard water with sodium ions. Since sodium compounds are soluble, the presence of sodium ions in water does not cause the white, scaly residues caused by calcium ions. However, calcium is more beneficial to human health than sodium because calcium is a necessary part of the human diet, while high levels of sodium intake are linked to increases in blood pressure. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recommends that adults ingest less than 2.4 g of sodium per day. How many liters of softened water, containing a sodium concentration of 0.050% sodium by mass, would a person have to consume to exceed the FDA recommendation? (Assume a water density of 1.0 g/mL.)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
First, we need to understand that the sodium concentration in the water is given as 0.050% by mass. This means that there are 0.050 grams of sodium in every 100 grams of water.
Next, we need to convert the FDA's recommended daily intake of sodium from grams to milligrams, because the concentration of sodium in the water is given in grams. So, 2.4 grams is equal to 2400 milligrams.
Then, we can calculate the amount of water that contains 2400 milligrams of sodium. Since there are 0.050 grams (or 50 milligrams) of sodium in 100 grams of water, we can set up a proportion to find the mass of water that contains 2400 milligrams of sodium. The proportion is 50 milligrams/100 grams = 2400 milligrams/x grams.
Solving for x in the proportion will give us the mass of water in grams that contains 2400 milligrams of sodium. Remember that 1 gram of water is approximately equal to 1 milliliter of water.
Finally, to find the volume of water in liters, we need to convert the volume from milliliters to liters. Since there are 1000 milliliters in a liter, we divide the volume in milliliters by 1000 to get the volume in liters.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
3mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Hard Water and Water Softeners
Hard water contains high concentrations of calcium and magnesium ions, which can lead to scale buildup in pipes and appliances. Water softeners work by exchanging these hard ions for sodium ions, which do not precipitate out and cause scaling. This process improves the quality of water for household use but alters its mineral content, impacting dietary intake.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Reaction with Water
Sodium Concentration and Mass Percent
Sodium concentration in a solution can be expressed as mass percent, which indicates the mass of sodium per 100 grams of solution. In this case, a 0.050% sodium by mass means that there are 0.050 grams of sodium in every 100 grams of softened water. Understanding this concept is crucial for calculating the total sodium intake from the volume of water consumed.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Mass Percent Calculation
Daily Sodium Intake Recommendations
The FDA recommends that adults limit their sodium intake to less than 2.4 grams per day to reduce the risk of hypertension and other health issues. This guideline is essential for evaluating how much softened water a person can safely consume without exceeding the recommended sodium limit, thereby ensuring a balance between hydration and health.
Recommended video:
Guided course
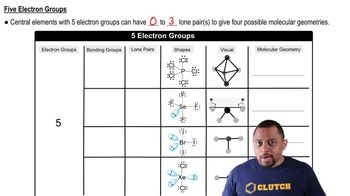
Molecular Geometry with Five Electron Groups
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1603
views
1
comments
Textbook Question
A gas has a Henry's law constant of 0.112 M>atm. What total volume of solution is needed to completely dissolve 1.65 L of the gas at a pressure of 725 torr and a temperature of 25 °C?
2238
views
3
rank
Textbook Question
The Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) sets a limit for mercury—a toxin to the central nervous system—at 0.0020 ppm by mass. Water suppliers must periodically test their water to ensure that mercury levels do not exceed this limit. Suppose water becomes contaminated with mercury at twice the legal limit (0.0040 ppm). How much of this water would a person have to consume to ingest 50.0 mg of mercury?
2219
views
Open Question
An aqueous solution contains 12.5% NaCl by mass. What mass of water (in grams) is contained in 2.5 L of the vapor above this solution at 55 °C? The vapor pressure of pure water at 55 °C is 118 torr. (Assume complete dissociation of NaCl.)
Open Question
The vapor above an aqueous solution contains 19.5 mg of water per liter of air at 25 °C. Assuming ideal behavior, what is the mole percent concentration of the solute in the solution?
Open Question
What is the freezing point of an aqueous solution that boils at 106.5 °C?
