Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Vapor Pressure
Vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by a vapor in equilibrium with its liquid or solid phase at a given temperature. It indicates how readily a substance will evaporate; higher vapor pressure means a substance evaporates more quickly. Water and acetone have different vapor pressures due to their molecular structures and intermolecular forces, affecting their evaporation rates.
Recommended video:
Raoult's Law and Vapor Pressure
Intermolecular Forces
Intermolecular forces are the forces of attraction or repulsion between molecules. They play a crucial role in determining the physical properties of substances, including boiling points and evaporation rates. Water has strong hydrogen bonding, while acetone has weaker dipole-dipole interactions, leading to acetone evaporating more quickly than water under identical conditions.
Recommended video:
Intermolecular vs Intramolecular Forces
Evaporation Rate
The evaporation rate is the speed at which molecules transition from the liquid phase to the vapor phase. Factors influencing evaporation include temperature, surface area, and intermolecular forces. In this scenario, acetone, with its lower boiling point and weaker intermolecular forces, will evaporate more quickly than water, despite the volume differences.
Recommended video:
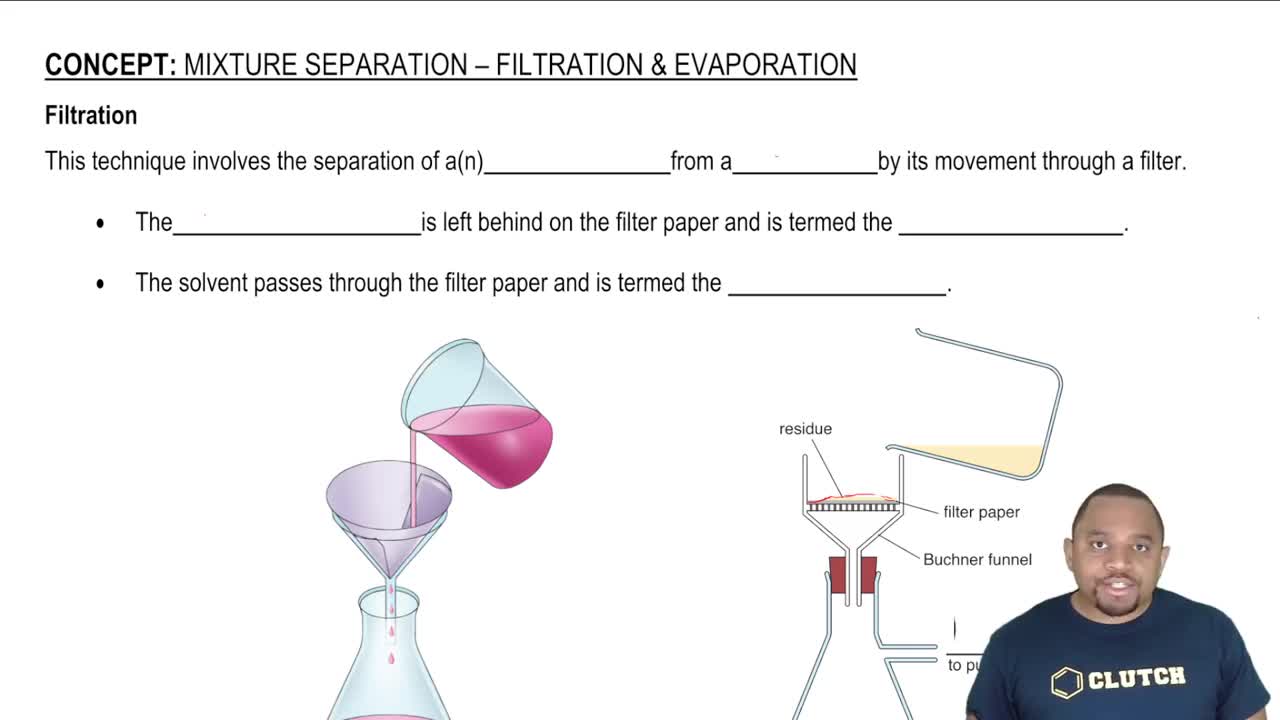
Filtration and Evaporation
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance