Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Band Gap
The band gap is the energy difference between the valence band and the conduction band in a solid material. It determines the electrical conductivity of the material; a small or nonexistent band gap allows electrons to move freely, making the material a good conductor. In contrast, a large band gap typically indicates an insulator or semiconductor.
Recommended video:
Intepreting the Band of Stability
Conductors vs. Semiconductors vs. Insulators
Materials are classified based on their ability to conduct electricity. Conductors, like metals, have little to no band gap, allowing electrons to flow easily. Semiconductors, such as silicon, have a moderate band gap that can be overcome under certain conditions, while insulators have a large band gap, preventing electron flow under normal circumstances.
Recommended video:
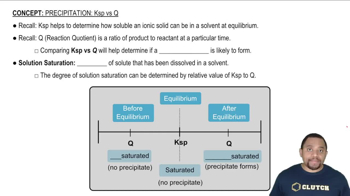
Ksp vs Q in Precipitation
Properties of Zn, Si, and As
Zinc (Zn) is a metal known for its conductive properties, typically exhibiting little to no band gap. Silicon (Si) is a semiconductor with a moderate band gap, while arsenic (As) can behave as a semiconductor or a metal depending on its allotrope. Understanding the electronic properties of these materials is crucial for predicting their behavior in terms of conductivity and band gap.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance