Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Activation Energy (Ea)
Activation energy (Ea) is the minimum energy required for a chemical reaction to occur. It represents the energy barrier that reactants must overcome to transform into products. In this context, a low Ea value, such as 6.3 kJ/mol, suggests that the reaction can proceed relatively easily, influencing the reaction rate and the conditions under which the reaction occurs.
Recommended video:
Molecular Geometry
Molecular geometry refers to the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule. The shape of a molecule, such as whether it is linear or bent, is determined by the number of bonding pairs and lone pairs of electrons around the central atom. For the ONF molecule, understanding its geometry is crucial for predicting its physical and chemical properties, including polarity and reactivity.
Recommended video:
Molecular Geometry with Two Electron Groups
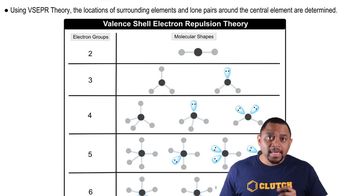
VSEPR Theory
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory is a model used to predict the geometry of molecules based on the repulsion between electron pairs. According to VSEPR, electron pairs will arrange themselves to minimize repulsion, leading to specific molecular shapes. In the case of ONF, the presence of lone pairs on the nitrogen atom influences the molecular shape, determining whether it is linear or bent.
Recommended video:
Molecular Shapes and VSEPR