Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Electron-Dot Structures
Electron-dot structures, also known as Lewis structures, represent the valence electrons of atoms within a molecule. They illustrate how electrons are shared or transferred between atoms, helping to visualize bonding and lone pairs. In the case of F3S¬S¬F, understanding the arrangement of fluorine and sulfur atoms is crucial for predicting molecular geometry.
Recommended video:
Lewis Dot Structures: Ions
Molecular Geometry
Molecular geometry refers to the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule. It is determined by the number of bonding pairs and lone pairs of electrons around the central atom, following the VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) theory. For F3S¬S¬F, identifying the geometry around the sulfur atoms is essential for understanding the overall shape of the molecule.
Recommended video:
Molecular Geometry with Two Electron Groups
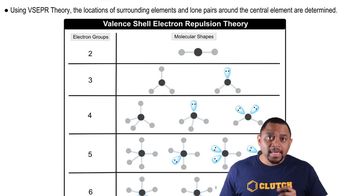
VSEPR Theory
VSEPR theory posits that electron pairs around a central atom will arrange themselves to minimize repulsion, leading to specific molecular shapes. This theory helps predict the geometry of molecules based on the number of bonding and non-bonding electron pairs. In the case of F3S¬S¬F, applying VSEPR will allow for the prediction of the angles and arrangement of the sulfur and fluorine atoms.
Recommended video:
Molecular Shapes and VSEPR