Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Hybridization
Hybridization is a concept in chemistry that describes the mixing of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals are used to explain the geometry of molecular bonding. The type of hybridization depends on the number of charge clouds (regions of electron density) around a central atom, which influences the shape and bond angles of the molecule.
Recommended video:
Charge Clouds
Charge clouds refer to regions around a central atom where electrons are likely to be found. These can be lone pairs, single bonds, or multiple bonds. The number of charge clouds determines the hybridization of the atom, as it influences the spatial arrangement of the orbitals and the resulting molecular geometry.
Recommended video:
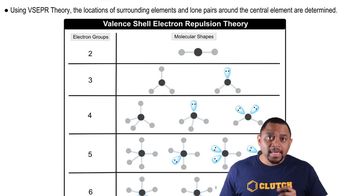
VSEPR Theory
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory is a model used to predict the geometry of individual molecules based on the repulsion between electron pairs. According to VSEPR, electron pairs will arrange themselves as far apart as possible to minimize repulsion, which directly relates to the number of charge clouds and the resulting hybridization of the central atom.
Recommended video:
Molecular Shapes and VSEPR
 McMurry 8th Edition
McMurry 8th Edition Ch.8 - Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure
Ch.8 - Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure Problem 60
Problem 60