Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Atomic Radius
Atomic radius refers to the size of an atom, typically measured from the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. As you move down a group in the periodic table, atomic radius increases due to the addition of electron shells. Conversely, across a period, atomic radius generally decreases due to increased nuclear charge, which pulls electrons closer to the nucleus.
Recommended video:
Ionic Radius
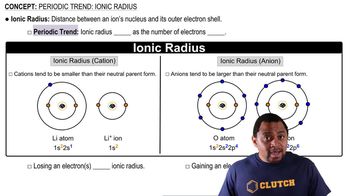
Ionic radius is the measure of an atom's ion in a crystal lattice. Cations (positively charged ions) are smaller than their neutral atoms because they lose one or more electrons, reducing electron-electron repulsion and allowing the remaining electrons to be pulled closer to the nucleus. Anions (negatively charged ions), like O2-, are larger than their neutral atoms due to the addition of electrons, which increases electron-electron repulsion.
Recommended video:
Electron Configuration and Stability
Electron configuration describes the distribution of electrons in an atom's orbitals. For oxygen, the neutral atom has six electrons, while O2- has eight, achieving a more stable electron configuration similar to that of noble gases. This added stability in anions often results in a larger ionic radius compared to their neutral counterparts, as the additional electrons increase repulsion among them.
Recommended video:
Electron Orbital Stability
 McMurry 8th Edition
McMurry 8th Edition Ch.6 - Ionic Compounds: Periodic Trends and Bonding Theory
Ch.6 - Ionic Compounds: Periodic Trends and Bonding Theory Problem 48
Problem 48