Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
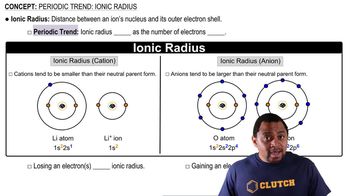
Ionic Radius
Ionic radius refers to the size of an ion in a crystal lattice. Cations, which are positively charged ions, are generally smaller than their neutral atoms due to the loss of electrons, which reduces electron-electron repulsion and allows the remaining electrons to be pulled closer to the nucleus. The ionic radius can vary significantly depending on the charge of the ion.
Recommended video:
Charge and Size Relationship
The charge of an ion directly affects its size. For cations, an increase in positive charge typically leads to a decrease in size. This is because a higher positive charge results in a stronger attraction between the nucleus and the remaining electrons, pulling them closer and reducing the overall size of the ion.
Recommended video:
Comparison of Cr3+ and Cr6+
In the case of chromium ions, Cr3+ has a +3 charge while Cr6+ has a +6 charge. Given the principles of ionic radius and charge, Cr3+ will be larger than Cr6+ because the lower positive charge of Cr3+ results in less nuclear attraction on the remaining electrons, allowing for a larger ionic size compared to the more highly charged Cr6+.
Recommended video:
Oxyacid Strength Comparison
 McMurry 8th Edition
McMurry 8th Edition Ch.6 - Ionic Compounds: Periodic Trends and Bonding Theory
Ch.6 - Ionic Compounds: Periodic Trends and Bonding Theory Problem 49
Problem 49