Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Electron Shells and Energy Levels
Elements in the periodic table are arranged according to their electron configurations, which are organized into shells or energy levels. Each shell can hold a specific maximum number of electrons, determined by the formula 2n², where n is the principal quantum number. This structure explains why the first shell holds 2 electrons, the second holds 8, and so forth.
Recommended video:
Number of Electrons in Shells
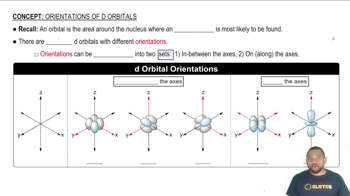
Subshells and Orbital Types
Within each electron shell, there are subshells (s, p, d, f) that further define the distribution of electrons. As you move to higher energy levels, additional subshells become available, allowing for more electrons to occupy the shell. For example, the third shell includes s and p subshells (totaling 8) and the d subshell (adding 10), leading to a total of 18 electrons.
Recommended video:
Periodic Trends and Grouping
The periodic table is structured in periods (rows) and groups (columns) that reflect similar chemical properties. The increase in the number of elements in successive periods (2, 8, 18, 32) corresponds to the filling of these electron shells and subshells, which influences the chemical behavior and reactivity of the elements. This systematic arrangement helps predict element properties based on their position in the table.
Recommended video: