Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Quantum Numbers
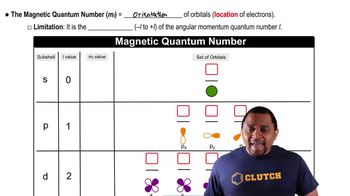
Quantum numbers are a set of numerical values that describe the unique quantum state of an electron in an atom. They include the principal quantum number (n), azimuthal quantum number (l), magnetic quantum number (m_l), and spin quantum number (m_s). Each quantum number provides specific information about the electron's energy level, shape, orientation, and spin.
Recommended video:
Azimuthal Quantum Number (l)
The azimuthal quantum number, denoted as 'l', determines the shape of an electron's orbital. It can take integer values from 0 to n-1, where n is the principal quantum number. For example, if l = 0, the orbital is spherical (s), and if l = 2, the orbital has a cloverleaf shape (d), which corresponds to four lobes.
Recommended video:
Orbital Shapes
Orbital shapes are defined by the values of the azimuthal quantum number (l). The shape of an orbital influences the distribution of electrons around the nucleus. For instance, the d orbitals, which have l = 2, are characterized by their cloverleaf shape, consisting of four lobes, allowing for complex interactions in chemical bonding and molecular geometry.
Recommended video:
Quantum Numbers and Orbital Shape Example