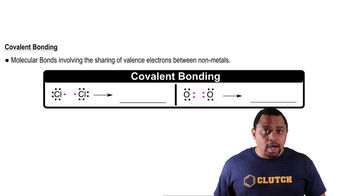
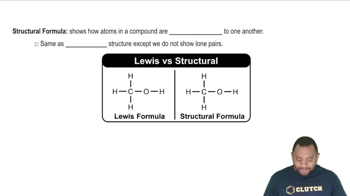
Open Question
Fumaric acid is an organic substance widely used as a food additive. Its elemental composition is 41.4% C, 3.5% H, and 55.1% O. A solution made by dissolving 0.1500 g of fumaric acid in water and diluting to a volume of 100.0 mL gave rise to an osmotic pressure of 240.3 mm Hg at 298 K. On titration of a sample weighing 0.573 g, 94.1 mL of 0.105 M NaOH was required to reach an equivalence point. Fumaric acid reacts with 1 mol of H2 to give a hydrogenation product. (a) What is the empirical formula of fumaric acid? (b) What is the molecular weight of fumaric acid? (c) Draw three possible structures for fumaric acid. (d) If fumaric acid contains a trans double bond, which of your structures is correct?