Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
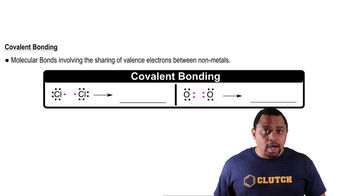
Covalent Bonding
Covalent bonding occurs when two atoms share pairs of electrons, allowing them to achieve a full outer shell and greater stability. In cyclohexane, each carbon atom forms four covalent bonds: two with hydrogen atoms and two with neighboring carbon atoms, creating a stable ring structure.
Recommended video:
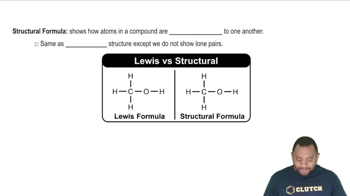
Structural Formula
A structural formula represents the arrangement of atoms within a molecule, showing how they are connected. For cyclohexane, the structural formula illustrates the six carbon atoms arranged in a ring, with each carbon bonded to two hydrogen atoms, emphasizing the molecule's cyclic nature.
Recommended video:
Cycloalkanes
Cycloalkanes are a class of hydrocarbons characterized by carbon atoms arranged in a ring structure, with single bonds between them. Cyclohexane, as a cycloalkane, has six carbon atoms and is notable for its stable conformation, which is crucial in various chemical reactions, including the synthesis of nylon.
Recommended video:
Rules for Naming Cyclic Alkanes
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance