Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
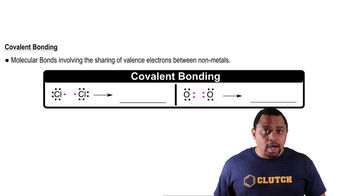
Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds are chemical bonds formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. In butane (C4H10), each carbon atom forms four covalent bonds, either with other carbon atoms or with hydrogen atoms. This sharing of electrons allows the atoms to achieve a more stable electron configuration, which is essential for the molecule's structure.
Recommended video:
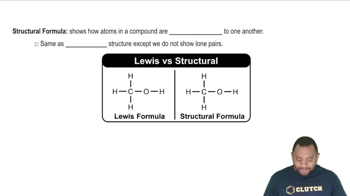
Structural Formula
The structural formula of a compound represents the arrangement of atoms within the molecule, showing how the atoms are connected. For butane, the structural formula illustrates the linear arrangement of four carbon atoms (C-C-C-C) and the associated hydrogen atoms. This visual representation is crucial for understanding the molecule's geometry and reactivity.
Recommended video:
Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons are organic compounds composed solely of carbon and hydrogen atoms. Butane is a type of hydrocarbon known as an alkane, characterized by single bonds between carbon atoms. Understanding hydrocarbons is fundamental in organic chemistry, as they serve as the building blocks for more complex molecules and are significant in various applications, including fuels.
Recommended video: