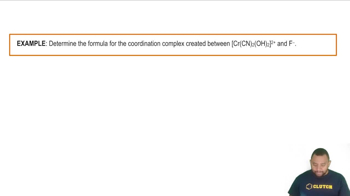
Nickel(II) complexes with the formula NiX2L2, where X is Cl- or N-bonded NCS- and L is the monodentate triphenylphosphine ligand P(C6H5)3, can be square planar or tetrahedral.
(c) Draw possible structures for each of the NiX2L2 complexes, and tell which ones have a dipole moment.