 McMurry 8th Edition
McMurry 8th Edition Ch.18 - Thermodynamics: Entropy, Free Energy & Equilibrium
Ch.18 - Thermodynamics: Entropy, Free Energy & Equilibrium Problem 125
Problem 125Is it possible for a reaction to be nonspontaneous yet exo-thermic? Explain.

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Spontaneity of Reactions

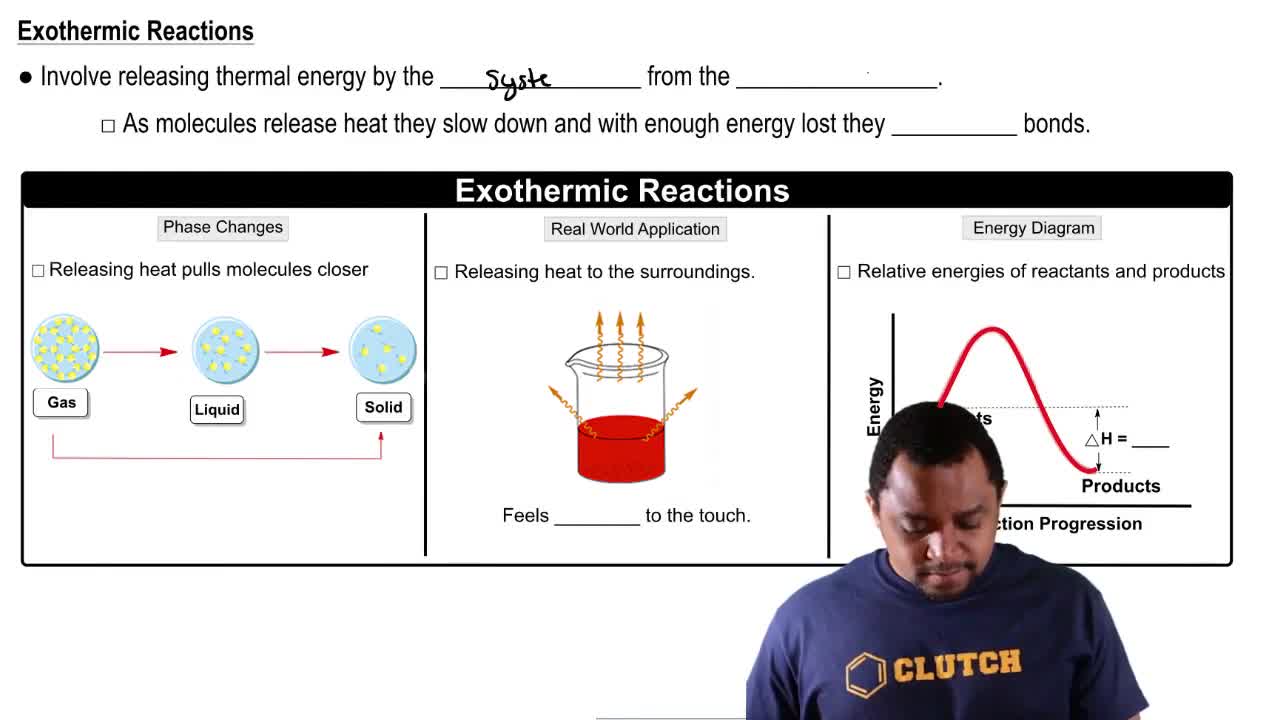
Exothermic Reactions
Gibbs Free Energy

Use the data in Appendix B to calculate the equilibrium pressure of CO2 in a closed 1 L vessel that contains each of the following samples: (a) 15 g of MgCO3 and 1.0 g of MgO at 25 °C Assume that ∆H° and ∆S° are independent of temperature.
Consider the Haber synthesis of gaseous NH3 (∆H°f = -46.1 kJ/mol; ∆G°f = -16.5 kJ/mol: (d) What are the equilibrium constants Kp and Kc for the reaction at 350 K? Assume that ∆H° and ∆S° are independent of temperature.
Trouton's rule says that the ratio of the molar heat of vaporization of a liquid to its normal boiling point (in kelvin) is approximately the same for all liquids: ∆Hvap/Tbp ≈ 88 J/(K*mol) (a) Check the reliability of Trouton's rule for the liquids listed in the following table.
Trouton's rule says that the ratio of the molar heat of vaporization of a liquid to its normal boiling point (in kelvin) is approximately the same for all liquids: ∆Hvap/Tbp ≈ 88 J/(K*mol) (b) Explain why liquids tend to have the same value of ∆Hvap/Tbp.