Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Neutralization Reaction
A neutralization reaction occurs when an acid reacts with a base to produce water and a salt. In this process, the acidic and basic properties cancel each other out, typically resulting in a solution that is closer to neutral pH, which is 7. The specific pH of the resulting solution depends on the strength of the acid and base involved.
Recommended video:
Lewis Dot Structures: Neutral Compounds
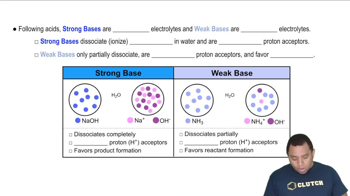
Strong vs. Weak Acids and Bases
Strong acids and bases completely dissociate in water, while weak acids and bases only partially dissociate. In the case of NaOH, a strong base, it fully dissociates to produce hydroxide ions. Benzoic acid, being a weak acid, does not fully dissociate, which affects the pH of the solution after neutralization.
Recommended video:
pH Scale
The pH scale measures the acidity or basicity of a solution, ranging from 0 to 14. A pH of 7 is considered neutral, below 7 is acidic, and above 7 is basic. The final pH after a neutralization reaction can be influenced by the relative strengths of the acid and base, determining whether the solution will be acidic, neutral, or basic.
Recommended video: