Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Neutralization Reaction
A neutralization reaction occurs when an acid reacts with a base to produce water and a salt. In this process, the acidic properties of the acid and the basic properties of the base are neutralized, typically resulting in a solution that is closer to neutral pH, which is 7. The specific pH of the resulting solution depends on the strength of the acid and base involved.
Recommended video:
Lewis Dot Structures: Neutral Compounds
Strong vs. Weak Acids and Bases
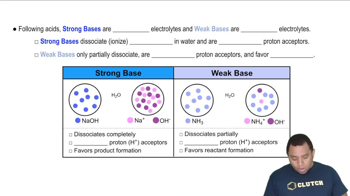
Acids and bases can be classified as strong or weak based on their ability to dissociate in water. Strong acids, like HBr, completely dissociate into ions, while weak bases, like aniline, only partially dissociate. This distinction is crucial in predicting the pH of the solution after neutralization, as the strength of the acid and base will influence the final pH.
Recommended video:
pH Scale
The pH scale measures the acidity or basicity of a solution, ranging from 0 to 14. A pH of 7 is considered neutral, below 7 is acidic, and above 7 is basic. Understanding the pH scale is essential for determining the outcome of a neutralization reaction, as it helps to assess whether the resulting solution is acidic, neutral, or basic based on the properties of the reactants.
Recommended video: