The following pictures represent solutions of three salts NaA (A- = X-, Y-, or Z-); water molecules and Na+ ions have been omitted for clarity.
(b) Which A- anion has the strongest conjugate acid?




The following pictures represent solutions of three salts NaA (A- = X-, Y-, or Z-); water molecules and Na+ ions have been omitted for clarity.
(b) Which A- anion has the strongest conjugate acid?
The following pictures represent solutions of three salts NaA (A- = X-, Y-, or Z-); water molecules and Na+ ions have been omitted for clarity.
(c) Which A- anion has the smallest value of pKb?
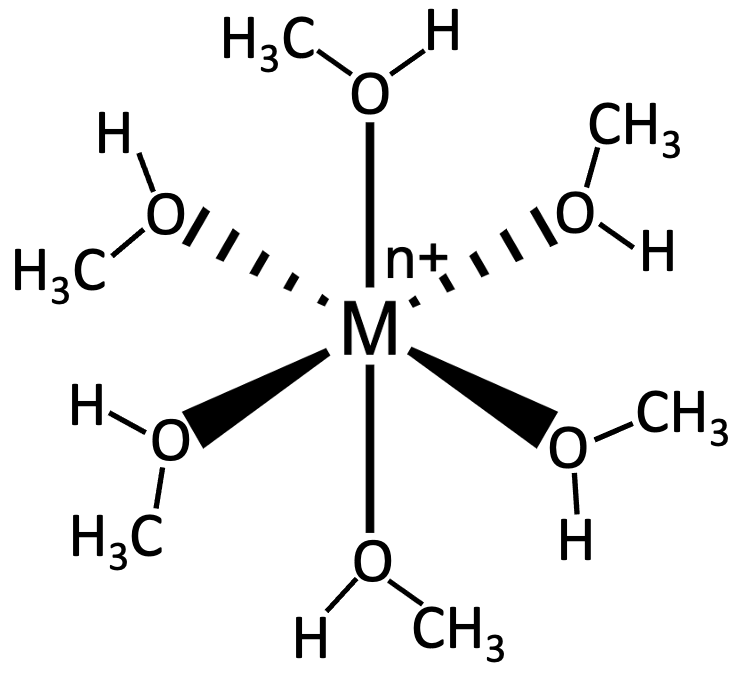
The following picture represents the hydrated metal cation M1H2O26 n + , where n = 1, 2, or 3.
(a) Write a balanced equation for the reaction of M1H2O26 n + with water and write the equilibrium equation for the reaction.
The following picture represents the hydrated metal cation M1H2O26 n + , where n = 1, 2, or 3. (c) Which M1H2O26n + ion 1n = 1,2, or 32 is the strongest acid, and which has the strongest conjugate base?