In aqueous solution, sodium acetate behaves as a strong electrolyte, yielding Na+ cations and CH3CO2 - anions. A particular solution of sodium acetate has a pH of 9.07 and a density of 1.0085 g/mL. What is the molality of this solution, and what is its freezing point?

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Electrolytes

pH and Acid-Base Chemistry

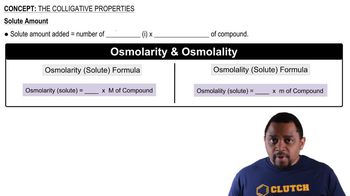
Colligative Properties
During a certain time period, 4.0 million tons of SO2 were released into the atmosphere and subsequently oxidized to SO3. As explained in the Inquiry, the acid rain produced when the SO3 dissolves in water can damage marble statues: CaCO3(s) + H2SO4(aq) → CaSO4(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) (a) How many 500 pound marble statues could be damaged by the acid rain? (Assume that the statues are pure CaCO3 and that a statue is damaged when 3.0% of its mass is dissolved.)
A 1.000 L sample of HF gas at 20.0 °C and 0.601 atm pressure was dissolved in enough water to make 50.0 mL of hydrofluoric acid. (a) What is the pH of the solution?
A 1.000 L sample of HF gas at 20.0 °C and 0.601 atm pressure was dissolved in enough water to make 50.0 mL of hydrofluoric acid. (b) To what volume must you dilute the solution to triple the percent dissociation?
