Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Liquid Crystals
Liquid crystals are substances that exhibit properties between those of liquids and solid crystals. They can flow like a liquid but have some degree of order in their molecular arrangement, which allows them to respond to electric or magnetic fields. This unique phase is crucial in applications like LCD screens, where the alignment of liquid crystal molecules can control light passage.
Recommended video:
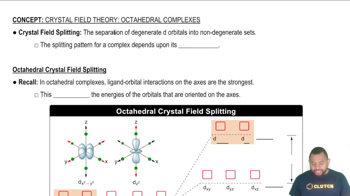
The crystal field splitting pattern for octahedral complexes has the d orbitals on or along the axes as having the higher energy.
Molecular Structure and Polarity
The molecular structure and polarity of a compound significantly influence its ability to form a liquid crystalline phase. Compounds with elongated, rod-like shapes and polar functional groups tend to exhibit liquid crystalline behavior due to their ability to align in a specific orientation. Understanding the molecular geometry helps predict the likelihood of liquid crystallinity.
Recommended video:
Phase Transitions
Phase transitions refer to the changes in the state of matter, such as from solid to liquid or liquid to gas. In the context of liquid crystals, the transition from a solid crystalline phase to a liquid crystalline phase occurs at specific temperatures, influenced by intermolecular forces. Recognizing these transitions is essential for determining the conditions under which a compound may exhibit liquid crystalline properties.
Recommended video:
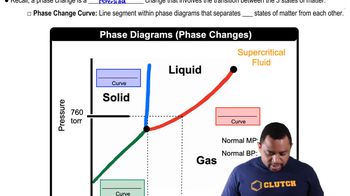
Phase Changes in Diagrams