Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molarity
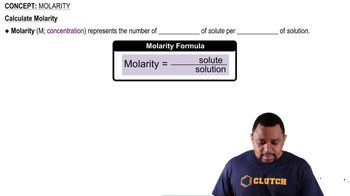
Molarity (M) is a measure of concentration defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. It is a crucial concept in chemistry for quantifying how much of a substance is present in a given volume of solution, allowing for calculations involving reactions and properties of solutions.
Recommended video:
Strong Acids and Ionization
Strong acids, like HClO4 (perchloric acid), completely dissociate in water, meaning that they release all of their hydrogen ions (H+) into the solution. This complete ionization is essential for determining the total molar concentration of ions, as each mole of a strong acid contributes an equivalent amount of H+ ions to the solution.
Recommended video:
Strong Acid-Strong Base Titration
Total Molar Concentration of Ions
The total molar concentration of ions in a solution is the sum of the concentrations of all ions present. For a strong acid like HClO4, which dissociates into H+ and ClO4- ions, the total concentration is calculated by adding the concentration of H+ ions to that of ClO4- ions, providing a complete picture of the ionic composition of the solution.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance