Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molarity
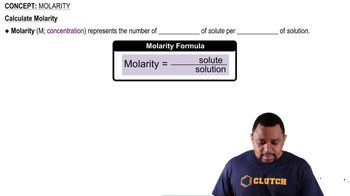
Molarity (M) is a measure of concentration defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. It is a crucial concept in chemistry for quantifying how much of a substance is present in a given volume of solution. In this case, a 1.250 M solution indicates that there are 1.250 moles of solute (CH3OH) in every liter of the solution.
Recommended video:
Dissociation of Solutes
Dissociation refers to the process by which a compound separates into its constituent ions or molecules when dissolved in a solvent. For ionic compounds, this results in the formation of free ions in solution, which contribute to the total molar concentration of ions. However, in the case of CH3OH (methanol), it does not dissociate into ions, as it is a molecular compound.
Recommended video:
Total Molar Concentration of Ions
The total molar concentration of ions in a solution is the sum of the concentrations of all individual ions present. For ionic compounds, this is straightforward as they dissociate into multiple ions. In contrast, for non-ionic compounds like CH3OH, the total molar concentration of ions is simply zero, as it does not produce any ions in solution.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance