Textbook Question
A solution of HCl in water conducts electricity, but a solu-tion of HCl in chloroform, CHCl3, does not. What does this observation tell you about how HCl exists in water and how it exists in chloroform?
1151
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

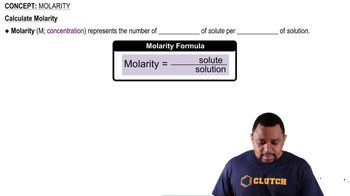

What is the total molar concentration of ions in each of the following solutions, assuming complete dissociation? (b) A 0.355 M solution of AlCl3
What is the total molar concentration of ions in each of the following solutions? (a) A 1.250 M solution of CH3OH
What is the total molar concentration of ions in each of the following solutions? (b) A 0.225 M solution of HClO4