For each of these contour representations of molecular orbitals, identify (c) whether the MO is bonding or antibonding (i)
The figure that follows contains ball-and-stick drawings of three possible shapes of an AF4 molecule. (a) For each shape, give the electron-domain geometry on which the molecular geometry is based. ii.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
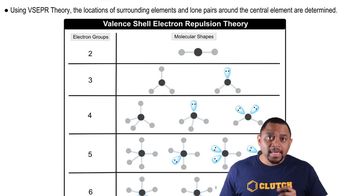
Key Concepts
Electron-Domain Geometry

Molecular Geometry

VSEPR Theory
For each of these contour representations of molecular orbitals, identify (a) the atomic orbitals (s or p) used to construct the MO (iii)
For each of these contour representations of molecular orbitals, identify (b) the type of MO (s or p) (iii)
For each of these contour representations of molecular orbitals, identify (b) the type of MO (s or p) (i)
For each molecule (a)–(f), indicate how many different electron-domain geometries are consistent with the molecular geometry shown. a.
The molecule shown here is difluoromethane 1CH2F22, which is used as a refrigerant called R-32. (c) If the molecule is polar, which of the following describes the direction of the overall dipole moment vector in the molecule: (i) from the carbon atom toward a fluorine atom, (ii) from the carbon atom to a point midway between the fluorine atoms, (iii) from the carbon atom to a point midway between the hydrogen atoms, or (iv) from the carbon atom toward a hydrogen atom?
