The figure that follows contains ball-and-stick drawings of three possible shapes of an AF4 molecule. (a) For each shape, give the electron-domain geometry on which the molecular geometry is based. ii.
Give the approximate values for the indicated bond angles in the following molecules: (c)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Bond Angles
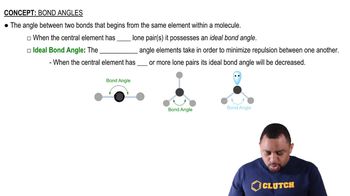
VSEPR Theory
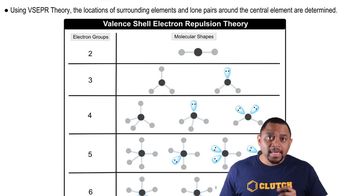
Molecular Geometry

The figure that follows contains ball-and-stick drawings of three possible shapes of an AF4 molecule. (c) Which of the following elements will lead to an AF4 molecule with the shape in (iii): Be, C, S, Se, Si, Xe? i.
ii.
iii.
Give the approximate values for the indicated bond angles in the following molecules: (a)
Give the approximate values for the indicated bond angles in the following molecules: (a)
Give the approximate values for the indicated bond angles in the following molecules: (d)
Ammonia, NH3, reacts with incredibly strong bases to produce the amide ion, NH2-. Ammonia can also react with acids to produce the ammonium ion, NH4+. (a) Which species (amide ion, ammonia, or ammonium ion) has the largest H¬N¬H bond angle? (b) Which species has the smallest H¬N¬H bond angle?
