Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
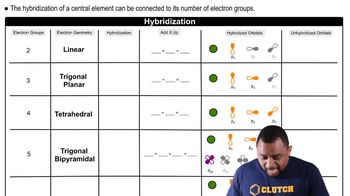
Electron-Domain Hybridization
Electron-domain hybridization is the process by which atomic orbitals mix to form new hybrid orbitals that can accommodate the electron pairs around a central atom. The type of hybridization (e.g., sp, sp2, sp3) depends on the number of electron domains, which include bonding pairs and lone pairs. Understanding this concept is crucial for predicting molecular geometry and the arrangement of atoms in a molecule.
Recommended video:
Hybridization and Electron Geometry
Molecular Geometry
Molecular geometry refers to the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule, which is determined by the repulsion between electron pairs surrounding the central atom. The VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) theory helps predict the geometry based on the number of bonding and lone pairs. This concept is essential for understanding the shape and polarity of molecules, which influences their chemical behavior.
Recommended video:
Molecular Geometry with Two Electron Groups
Dipole Moment
A dipole moment is a measure of the separation of positive and negative charges in a molecule, indicating its polarity. It arises when there is an uneven distribution of electron density, often due to differences in electronegativity between bonded atoms. Understanding dipole moments is important for predicting molecular interactions, solubility, and reactivity, as polar molecules behave differently than nonpolar ones.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance