A common form of elemental phosphorus is the tetrahedral P4 molecule, where all four phosphorus atoms are equivalent:
(b) How many P-P bonds are there in the molecule?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Molecular Structure

Covalent Bonds
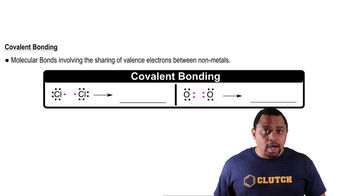
Counting Bonds
Acetylene (C2H2) and nitrogen (N2) both contain a triple bond, but they differ greatly in their chemical properties. (b) By referring to Appendix C, look up the enthalpies of formation of acetylene and nitrogen. Which compound is more stable?
Under special conditions, sulfur reacts with anhydrous liquid ammonia to form a binary compound of sulfur and nitrogen. The compound is found to consist of 69.6% S and 30.4% N. Measurements of its molecular mass yield a value of 184.3 g/mol. The compound occasionally detonates on being struck or when heated rapidly. The sulfur and nitrogen atoms of the molecule are joined in a ring. All the bonds in the ring are of the same length. (a) Calculate the empirical and molecular formulas for the substance.
A common form of elemental phosphorus is the tetrahedral P4 molecule, where all four phosphorus atoms are equivalent:
Draw a Lewis structure for a linear P4 molecule that satisfies the octet rule. Does this molecule have resonance structures?
Trifluoroacetic acid has the chemical formula CF3CO2H. It is a colorless liquid that has a density of 1.489 g/mL. (b) Trifluoroacetic acid can react with NaOH in aqueous solution to produce the trifluoroacetate ion, CF3COO2. Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction.
Trifluoroacetic acid has the chemical formula CF3CO2H. It is a colorless liquid that has a density of 1.489 g/mL. (d) How many milliliters of a 0.500 M solution of NaOH would it take to neutralize 10.5 mL of trifluoroacetic acid?
