Which neutral atom is isoelectronic with each of the following ions? Ga3+, Zr4+, Mn7+, I−, Pb2+.
Consider the isoelectronic ions F- and Na+. (d) For isoelectronic ions, how are effective nuclear charge and ionic radius related?

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Isoelectronic Ions

Effective Nuclear Charge (Z_eff)

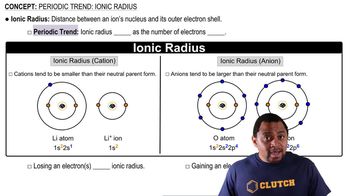
Ionic Radius
Some ions do not have a corresponding neutral atom that has the same electron configuration. For each of the following ions, identify the neutral atom that has the same number of electrons and determine if this atom has the same electron configuration. (a) CI−, (b) Sc3+, (c) Fe2+, (d) Zn2+, (e) Sn4+.
Consider the isoelectronic ions F- and Na+. (b) Using Equation 7.1 and assuming that core electrons contribute 1.00 and valence electrons contribute 0.00 to the screening constant, S, calculate Zeff for the 2p electrons in both ions.
Consider S, Cl, and K and their most common ions. (a) List the atoms in order of increasing size.
Consider S, Cl, and K and their most common ions.(c) Explain any differences in the orders of the atomic and ionic sizes.
