Consider the isoelectronic ions F- and Na+. (d) For isoelectronic ions, how are effective nuclear charge and ionic radius related?
Arrange each of the following sets of atoms and ions, in order of increasing size: (a) Pb, Pb2+, Pb4+

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Atomic Radius

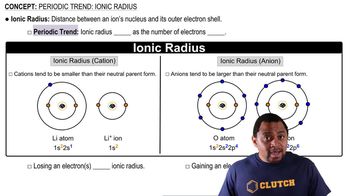
Ionic Radius
Charge and Size Relationship

Consider S, Cl, and K and their most common ions. (a) List the atoms in order of increasing size.
Consider S, Cl, and K and their most common ions.(c) Explain any differences in the orders of the atomic and ionic sizes.
Provide a brief explanation for each of the following.
K+ is larger than Na+.
In the ionic compounds LiF, NaCl, KBr, and RbI, the measured cation–anion distances are 201 pm (Li–F), 282 pm (Na–Cl), 330 pm (K–Br), and 367 pm (Rb–I), respectively. (b) Calculate the difference between the experimentally measured ion–ion distances and the ones predicted from Figure 7.8.
In the ionic compounds LiF, NaCl, KBr, and RbI, the measured cation–anion distances are 201 pm (Li–F), 282 pm (Na–Cl), 330 pm (K–Br), and 367 pm (Rb–I), respectively. (c) What estimates of the cation– anion distance would you obtain for these four compounds using neutral atom bonding atomic radii? Are these estimates as accurate as the estimates using ionic radii?
