Determine the oxidation number of sulfur in each of the following substances: (e) Locate sulfur in the periodic table in Exercise 4.47; what region is it in?
Ch.4 - Reactions in Aqueous Solution
Chapter 4, Problem 49c
Determine the oxidation number for the indicated element in each of the following substances: (c) P in AgPF6

Verified Solution
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Oxidation Number
The oxidation number, or oxidation state, is a theoretical charge assigned to an atom in a compound, reflecting its degree of oxidation or reduction. It helps in understanding electron transfer in redox reactions and is determined based on a set of rules, such as the oxidation state of elements in their elemental form being zero and the sum of oxidation states in a neutral compound being zero.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Oxidation Numbers
Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers
There are specific rules for assigning oxidation numbers, including that alkali metals are always +1, alkaline earth metals are +2, and fluorine is always -1. Oxygen typically has an oxidation number of -2, while hydrogen is usually +1. In polyatomic ions, the sum of the oxidation numbers must equal the charge of the ion, which is crucial for determining the oxidation state of elements in compounds.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Oxidation Number Rules
Complex Ions and Coordination Compounds
In coordination compounds like AgPF6, the central metal atom (Ag) is surrounded by ligands (PF6). The oxidation state of the central atom can be influenced by the charges of the ligands. Understanding how to analyze these compounds is essential for determining the oxidation state of the elements involved, as it requires knowledge of both the ligands' charges and the overall charge of the complex.
Recommended video:
Guided course
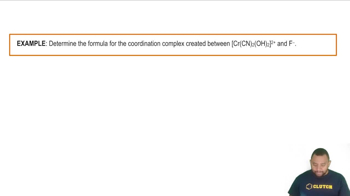
Coordination Complexes Example
Related Practice
Textbook Question
499
views
Textbook Question
Determine the oxidation number of sulfur in each of the following substances: (f) Which region(s) of the periodic table contains elements that can adopt both positive and negative oxidation numbers?
710
views
Textbook Question
Determine the oxidation number for the indicated element in each of the following substances: (a) S in SO3
354
views
Textbook Question
Determine the oxidation number for the indicated element in each of the following substances: (d) N in HNO3
399
views
Textbook Question
Determine the oxidation number for the indicated element in each of the following substances: (e) Pt in PtCl4
519
views
Textbook Question
Determine the oxidation number for the indicated element in each of the following substances: (f) Cl in NaClO4.
388
views
