Textbook Question
Determine the oxidation number for the indicated element in each of the following substances: (a) S in SO3
354
views



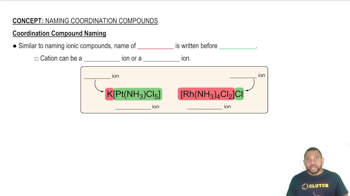
Determine the oxidation number for the indicated element in each of the following substances: (a) S in SO3
Determine the oxidation number for the indicated element in each of the following substances: (c) P in AgPF6
Determine the oxidation number for the indicated element in each of the following substances: (d) N in HNO3
Determine the oxidation number for the indicated element in each of the following substances: (f) Cl in NaClO4.
Which element is oxidized, and which is reduced in the following reactions? (a) N21g2 + 3 H21g2¡2 NH31g2
Which element is oxidized, and which is reduced in the following reactions? (b) 3 Fe1NO3221aq2 + 2 Al1s2¡3 Fe1s2 + 2 Al1NO3231aq2