The enzyme urease catalyzes the reaction of urea, (NH2CONH2), with water to produce carbon dioxide and ammonia. In water, without the enzyme, the reaction proceeds with a first-order rate constant of 4.15 × 10-5 s-1 at 100°C. In the presence of the enzyme in water, the reaction proceeds with a rate constant of 3.4 × 104 s-1 at 21°C. (b) If the rate of the catalyzed reaction were the same at 100°C as it is at 21°C, what would be the difference in the activation energy between the catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions?
Ch.14 - Chemical Kinetics

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 14, Problem 86c
The enzyme urease catalyzes the reaction of urea, (NH2CONH2), with water to produce carbon dioxide and ammonia. In water, without the enzyme, the reaction proceeds with a first-order rate constant of 4.15 × 10-5 s-1 at 100°C. In the presence of the enzyme in water, the reaction proceeds with a rate constant of 3.4 × 104 s-1 at 21°C. (c) In actuality, what would you expect for the rate of the catalyzed reaction at 100°C as compared to that at 21°C?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the reaction being catalyzed: Urea reacts with water to produce carbon dioxide and ammonia.
Understand that the rate of a reaction generally increases with temperature due to increased molecular motion and collision frequency.
Recognize that enzymes, like urease, are proteins that can denature at high temperatures, potentially reducing their catalytic activity.
Consider the Arrhenius equation, which relates the rate constant (k) to temperature (T): k = A * e^(-Ea/RT), where A is the pre-exponential factor, Ea is the activation energy, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvin.
Predict that while the rate constant for the catalyzed reaction at 100°C might be higher than at 21°C due to increased temperature, the enzyme's stability and activity at this higher temperature must also be considered, potentially leading to a decrease in the rate if the enzyme denatures.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Enzyme Catalysis
Enzyme catalysis refers to the process by which enzymes accelerate chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur. This allows reactions to proceed at a much faster rate compared to uncatalyzed reactions. Enzymes are highly specific and can significantly increase the rate of reactions under physiological conditions, making them essential for biological processes.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Catalyzed vs. Uncatalyzed Reactions
Rate Constants and Temperature
Rate constants are numerical values that indicate the speed of a reaction at a given temperature. According to the Arrhenius equation, the rate constant increases with temperature due to the increased kinetic energy of molecules, which leads to more frequent and effective collisions. Understanding how temperature affects rate constants is crucial for predicting reaction rates under different conditions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Rate Constant Units
First-Order Reactions
First-order reactions are those where the rate of reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of one reactant. This means that if the concentration of the reactant doubles, the reaction rate also doubles. The rate constant for first-order reactions is independent of the concentration of the reactant, making it a key concept in understanding how reaction rates change with the presence of catalysts and varying conditions.
Recommended video:
Guided course
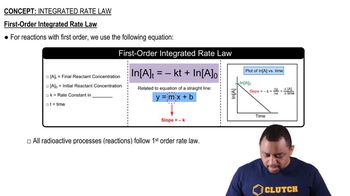
First-Order Reactions
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
The activation energy of an uncatalyzed reaction is 95 kJ/mol. The addition of a catalyst lowers the activation energy to 55 kJ/mol. Assuming that the collision factor remains the same, by what factor will the catalyst increase the rate of the reaction at (a) 25 C
4095
views
1
rank
Textbook Question
The activation energy of an uncatalyzed reaction is 95 kJ/mol. The addition of a catalyst lowers the activation energy to 55 kJ/mol. Assuming that the collision factor remains the same, by what factor will the catalyst increase the rate of the reaction at (b) 125 °C?
1218
views
