Americium-241 is used in smoke detectors. It has a first-order rate constant for radioactive decay of k = 1.6 * 10-3 yr-1. By contrast, iodine-125, which is used to test for thyroid functioning, has a rate constant for radioactive decay of k = 0.011 day-1. (c) How much of a 1.00-mg sample of each isotope remains after three half-lives?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
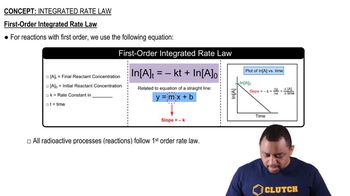
Radioactive Decay

Half-Life

First-Order Kinetics
Americium-241 is used in smoke detectors. It has a first-order rate constant for radioactive decay of k = 1.6 * 10-3 yr-1. By contrast, iodine-125, which is used to test for thyroid functioning, has a rate constant for radioactive decay of k = 0.011 day-1. (b) Which one decays at a faster rate?
The rate of a first-order reaction is followed by spectroscopy, monitoring the absorbance of a colored reactant at 520 nm. The reaction occurs in a 1.00-cm sample cell, and the only colored species in the reaction has an extinction coefficient of 5.60 * 103 M-1 cm-1 at 520 nm. (a) Calculate the initial concentration of the colored reactant if the absorbance is 0.605 at the beginning of the reaction.
The rate of a first-order reaction is followed by spectroscopy, monitoring the absorbance of a colored reactant at 520 nm. The reaction occurs in a 1.00-cm sample cell, and the only colored species in the reaction has an extinction coefficient of 5.60 * 103 M-1 cm-1 at 520 nm. (c) Calculate the half-life of the reaction.
The rate of a first-order reaction is followed by spectroscopy, monitoring the absorbance of a colored reactant at 520 nm. The reaction occurs in a 1.00-cm sample cell, and the only colored species in the reaction has an extinction coefficient of 5.60 * 103 M-1 cm-1 at 520 nm. (d) How long does it take for the absorbance to fall to 0.100?
