(a) What factors determine whether a collision between two molecules will lead to a chemical reaction?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
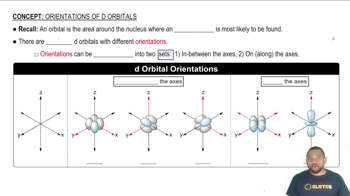
Collision Theory

Activation Energy

Molecular Orientation
The gas-phase decomposition of NO2, 2 NO21g2¡ 2 NO1g2 + O21g2, is studied at 383 C, giving the following data: Time (s) 3no2 4 (M) 0.0 0.100 5.0 0.017 10.0 0.0090 15.0 0.0062 20.0 0.0047 (c) Predict the reaction rates at the beginning of the reaction for initial concentrations of 0.200 M, 0.100 M, and 0.050 M NO2.
Sucrose 1C12H22O112, commonly known as table sugar, reacts in dilute acid solutions to form two simpler sugars, glucose and fructose, both of which have the formula C6H12O6. At 23 C and in 0.5 M HCl, the following data were obtained for the disappearance of sucrose: Time (min) 3C12H22o11 4 1M2 0 0.316 39 0.274 80 0.238 140 0.190 210 0.146 (a) Is the reaction first order or second order with respect to 3C12H22O114?
(b) Does the rate constant for a reaction generally increase or decrease with an increase in reaction temperature?
Calculate the fraction of atoms in a sample of argon gas at 400 K that has an energy of 10.0 kJ or greater.
