If you want to dope GaAs to make an n-type semiconductor with an element to replace Ga, which element(s) would you pick?
(b) Which of these molecules can be used as a monomer: ethanol, ethene (also called ethylene), methane?

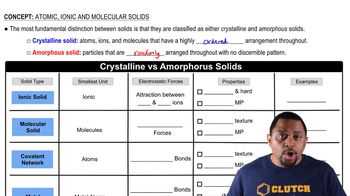
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Monomers and Polymers
Types of Hydrocarbons

Polymerization Process

Cadmium telluride is an important material for solar cells. (b) What wavelength of light would a photon of this energy correspond to?
Cadmium telluride is an important material for solar cells. (d) With respect to silicon, does CdTe absorb a larger or smaller portion of the solar spectrum?
Write a balanced chemical equation for the formation of a polymer via a condensation reaction from the monomers succinic acid 1HOOCCH2CH2COOH2 and ethylenediamine 1H2NCH2CH2NH22.
Write the chemical equation that represents the formation of (b) polyacrylonitrile from acrylonitrile (polyacrylonitrile is used in home furnishings, craft yarns, clothing, and many other items).
What molecular structural features cause high-density polyethylene to be denser than low-density polyethylene?
