Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Polymerization
Polymerization is a chemical process in which small molecules, known as monomers, chemically bond to form a larger, more complex structure called a polymer. In the case of polyacrylonitrile, the monomer acrylonitrile undergoes addition polymerization, where the double bond in the acrylonitrile molecule opens up to link with other monomers, creating long chains of polyacrylonitrile.
Acrylonitrile
Acrylonitrile is a colorless, volatile liquid that serves as a key monomer in the production of polyacrylonitrile. Its chemical structure features a vinyl group (C=C) and a nitrile group (C≡N), which allows it to participate in addition reactions. The presence of the nitrile group contributes to the polymer's properties, such as its strength and resistance to chemicals.
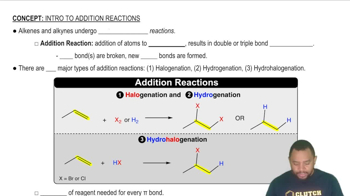
Addition Reaction
An addition reaction is a type of chemical reaction where two or more reactants combine to form a single product. In the context of polymerization, the addition reaction involves the breaking of double bonds in monomers, allowing them to link together. This reaction is crucial for forming polymers like polyacrylonitrile, as it enables the transformation of small monomer units into large, chain-like structures.
Recommended video: