Indicate whether each statement is true or false: (c) Nonmetallic elements are never found in alloys.
Ch.12 - Solids and Modern Materials
Chapter 12, Problem 48
An increase in temperature causes most metals to undergo thermal expansion, which means the volume of the metal increases upon heating. How does thermal expansion affect the unit cell length? What is the effect of an increase in temperature on the density of a metal?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
<Step 1: Understand Thermal Expansion> Thermal expansion refers to the increase in volume of a material as its temperature increases. For metals, this means that the atoms vibrate more vigorously and tend to occupy more space, leading to an expansion of the material's dimensions.
<Step 2: Relate Thermal Expansion to Unit Cell> In a crystalline solid, the smallest repeating unit is the unit cell. As the metal expands due to increased temperature, the dimensions of the unit cell, including its length, will also increase. This is because the atoms within the unit cell move slightly further apart.
<Step 3: Consider the Effect on Density> Density is defined as mass per unit volume (\( \rho = \frac{m}{V} \)). As the temperature increases, the volume of the metal increases due to thermal expansion, while the mass remains constant.
<Step 4: Analyze the Density Change> Since the volume increases and the mass stays the same, the density of the metal will decrease. This is because the same amount of mass is now spread over a larger volume.
<Step 5: Summarize the Effects> In summary, an increase in temperature causes the unit cell length of a metal to increase due to thermal expansion, and as a result, the density of the metal decreases because the volume increases while the mass remains constant.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Thermal Expansion
Thermal expansion refers to the increase in volume of a material as its temperature rises. In metals, this occurs because the increased kinetic energy of atoms causes them to vibrate more vigorously, leading to greater distances between them. This phenomenon is typically linear for solids, meaning that as temperature increases, the dimensions of the material, including length, width, and height, expand proportionally.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Thermal Equilibrium
Unit Cell Length
The unit cell is the smallest repeating unit in a crystal lattice that defines the structure of a solid. As temperature increases and thermal expansion occurs, the dimensions of the unit cell also increase, leading to a longer unit cell length. This change can affect the overall properties of the material, including its mechanical and thermal characteristics, as the arrangement of atoms within the unit cell is altered.
Recommended video:
Guided course
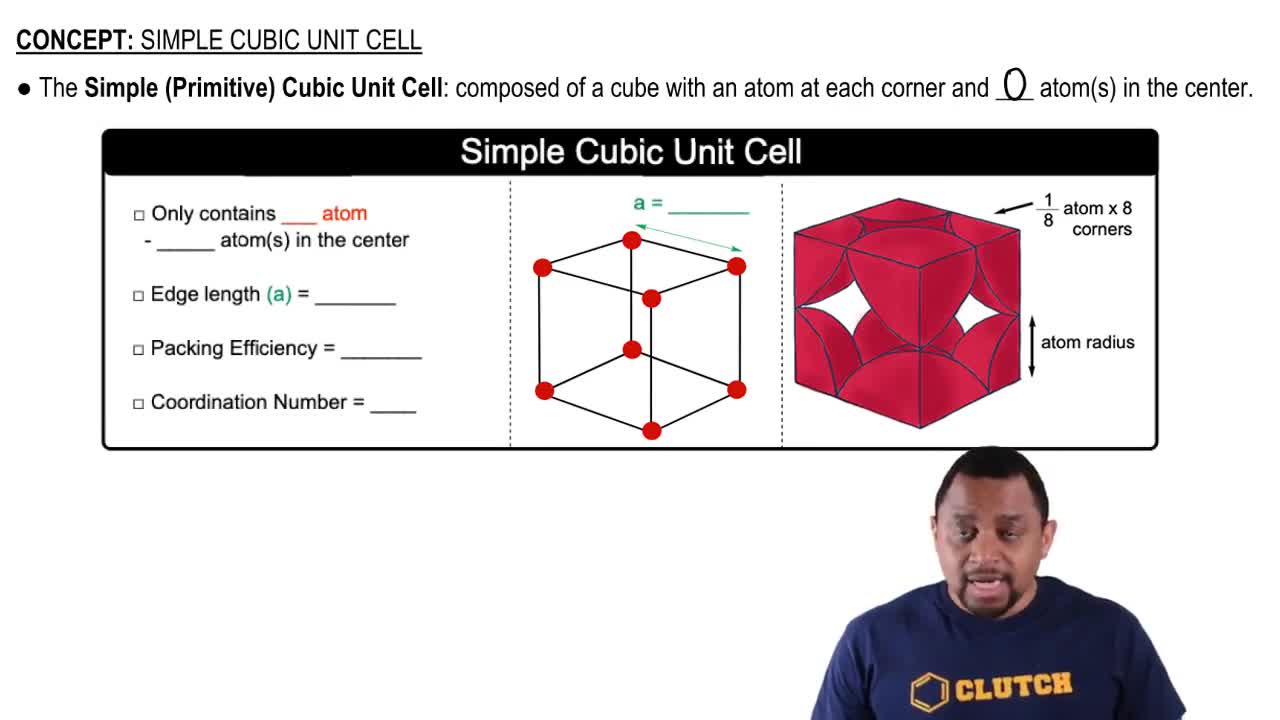
Simple Cubic Unit Cell
Density
Density is defined as mass per unit volume and is a critical property of materials. When a metal is heated and undergoes thermal expansion, its volume increases while its mass remains constant, leading to a decrease in density. This relationship is important in understanding how temperature changes can affect the buoyancy and structural integrity of metals in various applications.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Density Concepts
Related Practice
Textbook Question
394
views
Open Question
Indicate whether each statement is true or false: (a) Intermetallic compounds have a fixed composition. (b) Copper is the majority component in both brass and bronze. (c) In stainless steel, the chromium atoms occupy interstitial positions.
Textbook Question
Which element or elements are alloyed with gold to make
the following types of 'colored gold' used in the jewelry
industry? For each type, also indicate what type of alloy is
formed: (c) green gold.
802
views
Textbook Question
State whether each sentence is true or false: (b) Metals have high electrical conductivities because they are denser than other solids.
752
views
Textbook Question
The molecular-orbital diagrams for two- and four-atom linear chains of lithium atoms are shown in Figure 12.22. Construct a molecular-orbital diagram for a chain containing six lithium atoms and use it to answer the following questions: (a) How many molecular orbitals are there in the diagram?
696
views
Textbook Question
The molecular-orbital diagrams for two- and four-atom linear chains of lithium atoms are shown in Figure 12.22. Construct a molecular-orbital diagram for a chain containing six lithium atoms and use it to answer the following questions: (c) How many nodes are in the highest-energy molecular orbital?
618
views
