Textbook Question
(b) Could you measure the triple point of water by measuring the temperature in a vessel in which water vapor, liquid water, and ice are in equilibrium under 1 atm of air? Explain.
690
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
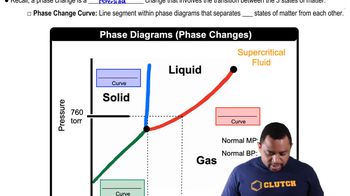


Referring to Figure 11.29, describe the phase changes (and the temperatures at which they occur) when CO2 is heated from -80 to -20°C at (a) a constant pressure of 3 atm,
The phase diagram for neon is
Use the phase diagram to answer the following questions. (a) What is the approximate value of the normal melting point?
At 25 °C gallium is a solid with a density of 5.91 g/cm3. Its melting point, 29.8 °C, is low enough that you can melt it by holding it in your hand. The density of liquid gallium just above the melting point is 6.1 g/cm3. Based on this information, what unusual feature would you expect to find in the phase diagram of gallium?