Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Mole Fraction
Mole fraction is a way of expressing the concentration of a component in a mixture. It is defined as the ratio of the number of moles of a specific component to the total number of moles of all components in the mixture. In this case, to find the mole fraction of CO2, you would divide the number of moles of CO2 by the total number of moles of all gases in the atmosphere.
Recommended video:
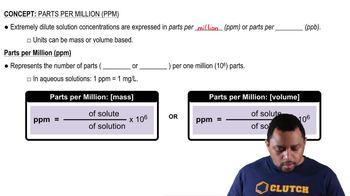
Parts Per Million (ppm)
Parts per million (ppm) is a unit of measurement used to describe the concentration of one substance in a million parts of another. In the context of gases in the atmosphere, 407 ppm of CO2 means that for every million air molecules, 407 are CO2. This measurement helps in understanding trace gas concentrations in the atmosphere.
Recommended video:
Ideal Gas Law
The Ideal Gas Law is a fundamental equation in chemistry that relates the pressure, volume, temperature, and number of moles of a gas. It is expressed as PV = nRT, where P is pressure, V is volume, n is the number of moles, R is the ideal gas constant, and T is temperature. This law can be useful for converting between different units of gas concentration and understanding the behavior of gases under various conditions.
Recommended video: