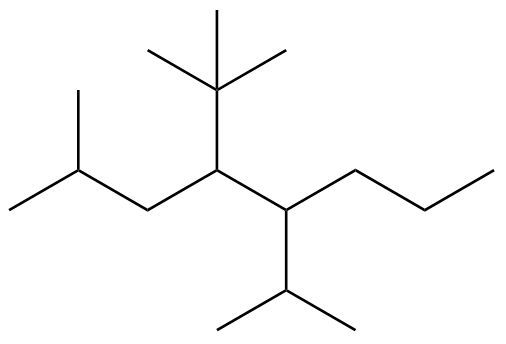
Here it says give the systematic name of the following alkane. Alright so to name this we're going to have to follow the given steps. O step one we find the longest carbon chain which is the parent chain and assign name according to the prefixes. Now if a tie between longest chain, choose the chain with more substituents.
Now, when it comes to finding along longest carbon chain, you have to let go of the fact that we're reading from left to right. When it comes to looking at an organic molecule, you may look left to right, may give you the longest chain, or right to left or top to bottom or bottom to top. You have to be able to look in all directions. So if we take a look here, what's the longest possible chain? Let's see, 1234 K, 123-4567 123-4567 O. It looks like there's two ways they give me 7.
And regardless of which way you go, if we went this way, we'd have two substituents, this one branching off and this one branching off. If we went the other way, it'd be the same thing. We're going this way. We have these two as substituents, all right, so our longest carbon chain is 7 carbons long. Now Step 2, assign names to all substituents, and this is important. Step three, start numbering the chain from the closest substituent. If a tie between substituents, compare the next closest substituent. If still a tie number in alphabetical order.
All right, so if we go down here, I've highlighted what we were just talking about, the longest carbon chain I decided highlighted this way. This gives me A7 carbon chain as the parent chain. And what's highlighted in orange are our substituents. So here we go, 123, we get to this substituent. We go 123, we get to this substituent. It's tied. Counting the carbon 3 from either side gets us to a substitute. But if we identify these, this is 1 carbon, so this would be a methyl group. This is 2 carbons, so this is an ethyl group.
We said if still a tie distance from the ends to the first substituent number in alphabetical order. E comes before M, which means we're going to number it this way, 123 and then 4567. Now step four, you're going to assign numbers, which gives us the location for each substituent when more than one identical substituents use the numerical prefixes of die for two, try for three, and Tetra for four.
Alright, so we have on carbon #3 ethyl. So this we're going to say we're going to use 3 ethyl OK name substituents in alphabetical order. Prefixes do not count. Use commas to separate numbers from numbers. And we're going to use dashes to separate letters from numbers. Letters are not separated from letters, so a lot is being said here. So let's work this out. We're going to name the substituents alphabetically, and we're going to give their number locations. So Ethyl is on carbon #3, so that's three. And remember, we're going to use dashes to separate letters from numbers. SO3 dash.
Ethel methyls on carbon #5-5 methyl and then we have A7 carbon chain. 7 carbons is Hept and it's an alkane so it's hep tane. So this would be the name of this alkyl group or this this alkane molecule 3 ethyl 5 methyl heptane. This would be our final answer. Again, it gets a little bit drawing in terms of naming these types of molecules, but with enough practice it becomes second nature O keep at it and you'll get to master naming all these different types of organic compounds.