9. Quantum Mechanics
Bohr Model
9. Quantum Mechanics
Bohr Model
Additional 4 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 7 of 7 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Which of the electron transitions represents absorption with the greatest frequency?
3508views11rank - Multiple Choice
Which of the following transitions (in a hydrogen atom) represent emission of the shortest wavelength?
5786views6rank2comments - Multiple Choice
If the energy of an electron within the boron atom was calculated as –6.0556 x 10-18 J, at what energy level would it reside?
1779views4rank3comments - Multiple ChoiceWhich of the following statements about the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom is false?881views
- Open Question
An atomic emission of light with a specific amount of energy from an atom confirms that
1099views - Open Question
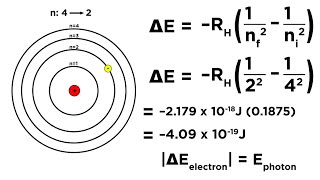
How much energy does the electron have initially in the n=4 excited state
943views - Open QuestionWhich of the following transitions (in a hydrogen atom) represent absorption of the smallest frequency photon?1201views
- Open QuestionDetermine whether each of the following transitions in the hydrogen atom corresponds to absorption or emission of energy.747views