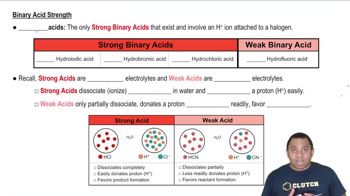
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Titration Curves
Titration curves graphically represent the change in pH of a solution as a titrant is added. In this case, the curves show the titration of a strong base (NaOH) with a weak acid. The shape of the curve indicates the buffering region and the equivalence point, where the amount of acid equals the amount of base added.
Recommended video:
Acid-Base Titration Curves
pKa and Acid Strength
The pKa value is a measure of the strength of an acid in solution, defined as the negative logarithm of the acid dissociation constant (Ka). For weak acids, the pKa is typically found at the midpoint of the steepest part of the titration curve, where half of the acid has been neutralized, indicating the concentration of the acid equals that of its conjugate base.
Recommended video:
Equivalence Point
The equivalence point in a titration is reached when the amount of titrant added is stoichiometrically equivalent to the amount of substance being titrated. For weak acids, this point is characterized by a rapid change in pH, and it is crucial for determining the pKa, as it indicates the complete neutralization of the acid by the base.
Recommended video: