Textbook Question
Indicate whether each statement is true or false. (c) Increasing the reaction temperature increases the fraction of successful collisions between reactants.
525
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


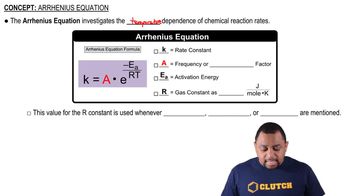
Indicate whether each statement is true or false. (c) Increasing the reaction temperature increases the fraction of successful collisions between reactants.
Indicate whether each statement is true or false. (a) If you measure the rate constant for a reaction at different temperatures, you can calculate the overall enthalpy change for the reaction.
Indicate whether each statement is true or false. (b) Exothermic reactions are faster than endothermic reactions.
Based on their activation energies and energy changes and assuming that all collision factors are the same, rank the following reactions from slowest to fastest. (a) Ea = 45 kJ>mol; E = -25 kJ>mol (b) Ea = 35 kJ>mol; E = -10 kJ>mol (c) Ea = 55 kJ>mol; E = 10 kJ>mol